How to be an Effective Caregiver After A Hip Fracture

A hip fracture is a serious and often life-changing injury, especially for older adults. It typically occurs due to falls, weakened bones, or sudden trauma. Recovery can be challenging, and proper treatment is essential to prevent complications. But how long does it take to heal? Can you still walk with a fractured hip? This guide covers everything you need to know, from symptoms and treatment options to the recovery process and ways to reduce risks.
What is a Hip fracture?
A hip fracture is a break or a crack in the upper part of the femur bone (thigh bone) that forms the hip joint. This type of injury is common among older adults and usually occurs due to a fall, particularly in those with weaker bones due to osteoporosis. Hip fractures can be severe, especially for older adults, and may require surgery and rehabilitation to heal properly.
Types of hip fractures
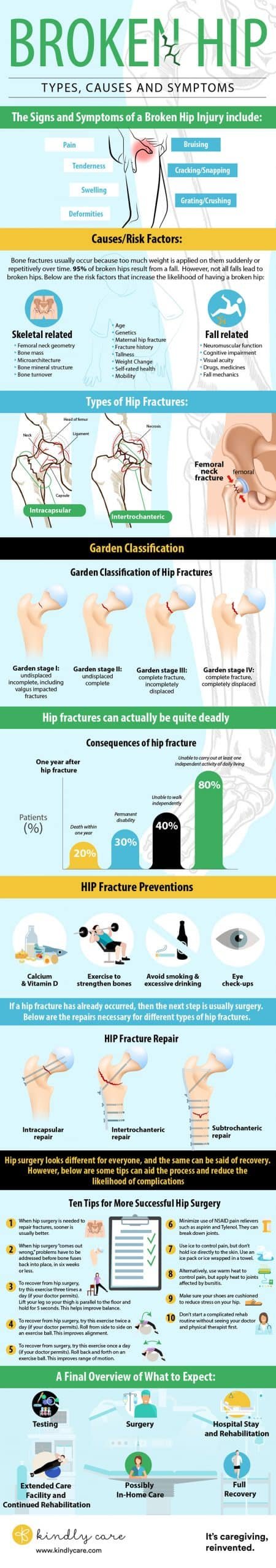
Hip fractures can be serious, especially for older adults. Here are the common types:
-
Femoral Neck Fracture: This break happens just below the ball of the hip joint. It’s common in older adults with osteoporosis and can affect mobility.
-
Intertrochanteric Fracture: This occurs between the neck and shaft of the thigh bone (femur). Surgery is usually needed to fix it.
-
Subtrochanteric Fracture: This type of fracture happens in the upper femur, just below the intertrochanteric region, and often requires surgery.
-
Hairline Hip Fracture: A small crack in the hip bone that might not cause immediate pain but can worsen if left untreated.
Hip fractures can cause severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving or bearing weight on the affected leg. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a hip fracture.
Causes of Hip Fracture
There are several reasons why seniors are more prone to falls and hip fractures:
Osteoporosis:
As mentioned earlier, osteoporosis is a common condition in seniors, making bones weaker and more brittle, making them more prone to fractures even with minor impacts.
Age-related changes:
Aging causes changes in the body, such as decreased muscle mass and strength, reduced balance, and coordination, which can increase the risk of falls.
Medications:
Many seniors take medications for various health conditions affecting balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls. These medications include sedatives, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and blood pressure-lowering drugs.
Vision and hearing problems:
Poor vision or hearing can make it challenging for seniors to detect potential hazards or obstacles, making them more susceptible to falls.
Environmental hazards:
Tripping hazards like loose rugs, cluttered floors, uneven surfaces, inadequate lighting, and lack of grab bars in the bathroom can increase the risk of falls.
Chronic diseases:
Seniors with chronic conditions like Parkinson’s, dementia, and stroke are at higher risk of falls due to their effects on balance and mobility.
Lack of physical activity:
Seniors who are not physically active tend to have weaker muscles and poor balance, increasing their risk of falls.
Reducing the risk of falls and hip fractures requires a multi-faceted approach, including regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, reducing environmental hazards, and monitoring medication use by a healthcare professional.
Here are a few other things to consider
- Poor nutrition: Improper nutrition makes the elderly susceptible to hip fractures later in life. Also, eating disorders can cause severe damage to our bones.
- Medications: Taking four or more medicines at a time can increase the chances of hip fracture in old age.
- Alcohol and Tobacco: Long-term use of alcohol and tobacco can cause the bones to weaken.
- Illnesses: Certain medical conditions can make seniors more susceptible to Hip fractures. Some of these include rheumatoid diseases, dementia, and also depression.
- Lack of Coordination: Poor balance is the primary reason behind most hip fractures.
Symptoms of Hip Fracture
A broken hip or fracture can cause several signs and symptoms, including:
Severe pain in the Hip or groin area:
This pain may be intense and may worsen with movement or weight-bearing.
Swelling and bruising:
The affected area may appear swollen and bruised due to bleeding or inflammation.
Limited mobility:
The person may have difficulty moving the leg or experience a limp when walking.
Inability to bear weight:
A person with a hip fracture may be unable to put weight on the affected leg or experience pain.
Shorter leg:
The affected leg may appear more straightforward than the unaffected leg.
External rotation of the leg:
The leg may appear to be rotated outward or to the side.
Numbness or tingling:
Some people may experience numbness or tingling in the affected leg or foot.
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms after a fall or trauma to the Hip, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve the chances of a successful recovery.
Caring for your loved one with a hip fracture is difficult. First, caregivers need to understand their condition. Often, your loved one can immediately figure out after a fall that they have a broken hip or fracture. If the head of the hip bone is damaged, the pain is less and often gets ignored.
Why do hip fractures affect our aging population the most?
Hip fractures affect the aging population more than any other age group because our bones become weaker and more brittle as we age, a condition known as osteoporosis. Osteoporosis can cause bones to become thin, porous, and fragile, increasing the risk of fractures from falls or even minor impacts.
As we age
your bodies undergo physical changes that affect your balance, coordination, and mobility, making us more prone to falls. Additionally, many older adults may have other health conditions or take medications that can increase the risk of falls, such as vision problems, muscle weakness, balance disorders, and dizziness.
Hip fractures can be severe for older adults
They may lead to prolonged hospitalization, complications, and decreased mobility and independence. Therefore, older adults must reduce their risk of falls, such as staying physically active, improving their balance and strength, using assistive devices when necessary, and making their homes safer by removing tripping hazards and improving lighting.
Treatment Options for Hip Fractures
The treatment for a hip fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s health status. Hip fractures generally require surgical intervention to repair the broken bone and restore mobility. Here are some of the standard treatment options for hip fractures:
Surgical Treatments
Surgical intervention is often necessary to repair the fractured bone, restore function, and reduce pain. The choice of surgery depends on the type of fracture and the patient’s health condition
Hip replacement surgery involves removing the damaged parts of the hip joint and replacing them with artificial components. Hip replacement surgery is typically recommended for older adults with more severe fractures, pre-existing joint disease, or hip fractures that cannot be repaired.
Internal fixation: In this procedure, metal screws, pins, or plates hold the broken bone in place while it heals. Internal fixation is typically recommended for younger adults with stable fractures.
Partial hip replacement: This procedure involves replacing only the ball portion of the hip joint, leaving the socket intact. Partial hip replacement is typically recommended for patients with certain hip fractures.
Post-Surgical Recovery
Proper recovery is crucial to ensuring long-term success after surgery. Rehabilitation and other recovery measures play a significant role in healing and regaining independence.
Rehabilitation: After surgery, patients usually require repair to regain strength, mobility, and independence. Restoration may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other supportive measures.
Pain management: Pain management is integral to treating a hip fracture and may include medication, nerve blocks, or other treatments as appropriate.
It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for individualized treatment recommendations, as treatment will depend on the individual’s specific condition and medical history.
How is hip replacement surgery performed?
Hip replacement surgery, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves removing the damaged or diseased parts of the hip joint and replacing them with artificial components. Here are the general steps involved in the procedure:
- Anesthesia: Before the surgery, patients will be given anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure.
- Incision: A large incision is made on the side of the hip to allow access to the joint.
- Preparation of the joint: The damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint using special surgical tools.
- Insertion of the prosthesis: The artificial components are inserted into the hip joint. The prosthesis typically consists of a metal or ceramic ball attached to a stem placed into the thigh bone and a socket placed into the hip bone. The components are usually held in place using cement or are designed to allow the bone to grow into them.
- Closing the incision: Once the prosthesis is in place, the incision is closed using stitches or staples.
- Postoperative care: After the surgery, the patient will be closely monitored and likely need to stay in the hospital for a few days. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are usually required to help the patient regain strength, mobility, and independence.
Hip replacement surgery is a major surgical procedure that carries some risks and complications, such as infection, blood clots, dislocation of the prosthesis, and implant wear or loosening. It is essential to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified healthcare professional before deciding to undergo surgery.
How is rehabilitation going to help with the hip fracture?
Rehabilitation is an essential component of the recovery process after a hip fracture. Here are some ways in which rehabilitation can help:
Restoring mobility:
Rehabilitation can help restore mobility to the affected hip joint, allowing patients to regain the ability to walk, stand, and perform other activities of daily living.
Improving strength and flexibility:
Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip joint and improve flexibility, which can help prevent future injuries and improve overall bodily function.
Pain management:
Rehabilitation can help manage pain associated with hip fractures, both during recovery and in the long term.
Enhancing balance and coordination:
Rehabilitation can help improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and other injuries.
Preventing complications:
Rehabilitation can help avoid complications associated with immobility, such as blood clots, pressure sores, and muscle weakness.
Rehabilitation typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other supportive measures and is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. Therefore, working closely with a qualified healthcare professional to develop a rehabilitation plan appropriate for the individual’s condition and medical history is essential.
Tips for the caregiver to help their loved ones
If you are a caregiver for a loved one who has suffered a hip fracture, there are several things you can do to help them during their recovery:
Help with mobility
Your loved one may have difficulty getting around after their surgery, so it is essential to assist with mobility. This may include helping them get in and out of bed, helping them use a walker or crutches, and providing service with other activities of daily living.
Provide emotional Support
Recovering from a hip fracture can be physically and emotionally challenging. Therefore, it is crucial to provide emotional support to your loved one during this time, listening to their concerns and providing reassurance and encouragement.
Manage medications
Your loved one may need a prescription to manage pain or prevent infection after surgery. Help them keep track of their medications and ensure they take them as prescribed.
Assist with rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is integral to recovering after a hip fracture. Help your loved one attend physical and occupational therapy sessions, and encourage them to perform their prescribed exercises and activities.
Promote a healthy lifestyle
Encourage your loved one to eat a healthy diet, stay hydrated, and exercise as their healthcare provider recommends. These habits can promote healing and overall wellbeing.
Ensure a safe environment
Falls can be a significant concern for older adults with hip fractures. Help ensure your loved one’s home is free of hazards that could increase the risk of falls, such as loose rugs, cluttered walkways, or poor lighting.
Take care of yourself
Caregiving can be a demanding and stressful role. Therefore, taking care of yourself by getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet, and seeking support from others as needed is essential.
Other things to consider
- Exercising: With the caregiver’s help, exercise is vital to regaining muscle strength quicker.
- Assisted devices: Assisted devices are crucial for the wellbeing of the elderly. For example, you are wearing disposable underwear, a walker, a wheelchair, grab bars, and a bath chair.
- Please do not leave them alone: Assist them in bathing and daily living.
- Clothing and Footwear: Wear loose-fitting clothing that can fasten in the front—slip-on footwear with anti-slip soles for easy, risk-free walking.
- Try and keep depression at bay: The sudden loss of freedom makes them depressed, irritable and incapacitated. So, the caregivers must empathize with them.
- Get some fresh air: A daily ride to the park, where they can meet their friends. And getting some fresh air would make the senior feel much better.
A little love and support and lots of care can give the senior the gift of living a fulfilling life. All these tips can ensure a faster recovery from hip surgery and help them live a happy and healthy life.
Emotional Wellbeing after hip surgery
Hip surgery can be a challenging and stressful experience, and it is not uncommon for patients to experience a range of emotions after the procedure. Here are some tips for promoting emotional wellbeing during the recovery process:
Recognize your feelings
It is essential to acknowledge and accept them, whether positive or negative. Allow yourself to feel the emotions that come up and healthily express them.
Practice self-care
Take care of yourself by getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in enjoyable activities. Self-care can help reduce stress and improve overall wellbeing.
Seek support
Lean on friends, family members, or a support group for emotional support. Talking with others who have been through a similar experience can help you feel less alone and more understood.
Set realistic expectations
Recovery from hip surgery can be slow and gradual, and you must set realistic expectations for yourself. Be patient with yourself and celebrate small victories along the way.
Stay positive
Maintaining a positive outlook can help improve mood and reduce stress. Focus on the progress you are making and the things you can do rather than dwelling on the things you can’t.
Stay engaged
Engage in activities that keep you mentally stimulated and socially connected, such as reading, watching movies, or spending time with loved ones. Staying engaged can help improve mood and promote overall wellbeing.
If you are experiencing persistent sadness, anxiety, or hopelessness, it may be helpful to talk to a mental health professional for additional support.
Conclusion
A hip fracture is a common and serious injury among the aging population, and caring for someone who has suffered one can be challenging and stressful. However, with knowledge and support, caregivers can help their loved ones recover and remain independent. Caregivers should also prioritize their self-care to ensure they can provide adequate clearance over the long term. By working with healthcare providers and providing compassionate care, caregivers can help older adults recover from hip fractures and maintain independence and quality of life.

Hip fractures are indeed a significant concern, especially for older adults. It’s alarming how a simple fall can lead to such severe consequences. I appreciate how the article highlights the importance of addressing osteoporosis and other risk factors. Regular exercise and a healthy diet seem like small steps that can make a big difference in preventing these injuries. Do you think that more awareness campaigns are needed to educate seniors about fall prevention strategies? What are your thoughts?
Thank you so much for your thoughtful comment — I couldn’t agree more. Hip fractures can be life-altering for older adults, and the ripple effects on mobility, independence, and overall health are often underestimated.
Yes, I absolutely believe more awareness campaigns are needed — not just for seniors, but for caregivers and families too. Fall prevention isn’t just about “being careful,” it’s about creating safer environments, strengthening the body through balance-focused exercise, and proactively managing conditions like osteoporosis before a fall happens.
We also need to normalize talking about these risks early — not after an injury occurs. Small, consistent steps like strength training, vitamin D and calcium-rich diets, regular vision checks, and home safety adjustments can make a world of difference.
Thank you again for raising this important point — together, we can continue spreading knowledge that truly empowers aging adults and their caregivers to stay safe and strong.